Abstract:
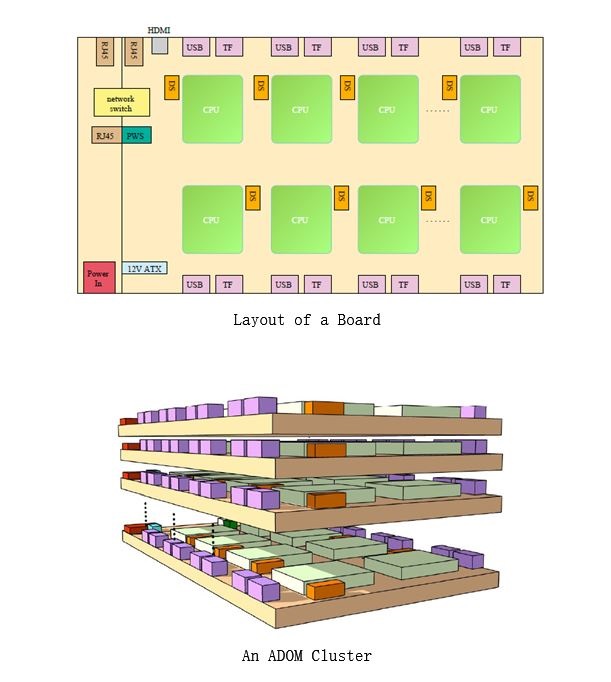
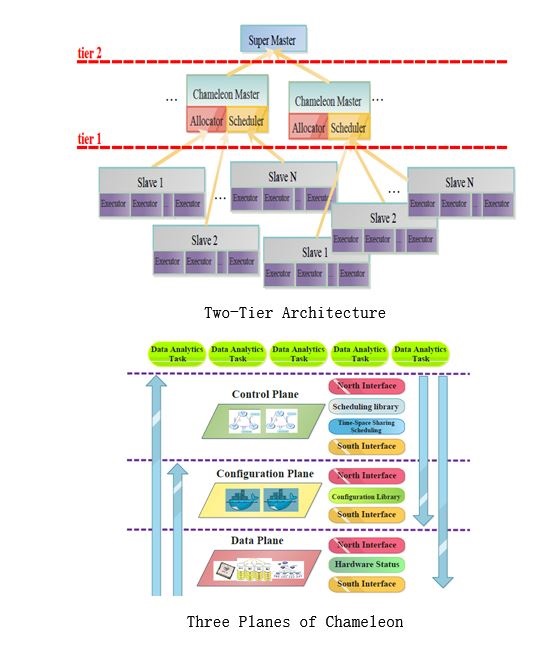
Recently, analyzing big data on the move is booming. It requires that the hardware resource should be low volume, low power, light in weight, high-performance, and highly scalable whereas the management software should be flexible and consume little hardware resource. To meet these requirements, we present a system named SOCA-DOM that encompasses a mobile system-on-chip array architecture and a two-tier “software-defined” resource manager named Chameleon. First, we design an Ethernet communication board to support an array of mobile system-on-chips. Second, we propose a two-tier software architecture for Chameleon to make it flexible. Third, we devise data, configuration, and control planes for Chameleon to make it “software-defined” and in turn consume hardware resources on demand. Fourth, we design an accurate synthetic metric that represents the computational power of a computing node. We employ 12 Apache Spark benchmarks to evaluate SOCA-DOM. Surprisingly, SOCA-DOM consumes up to 9.4x less CPU resources and 13.5x less memory than Mesos which is an existing resource manager. In addition, we show that a 16-node SOCA-DOM consumes up to 4x less energy than two standard Xeon servers. Based on the results, we conclude that an array architecture with fine-grained hardware resources and a software-defined resource manager works well for analyzing big data on the move.


 下载:
下载: