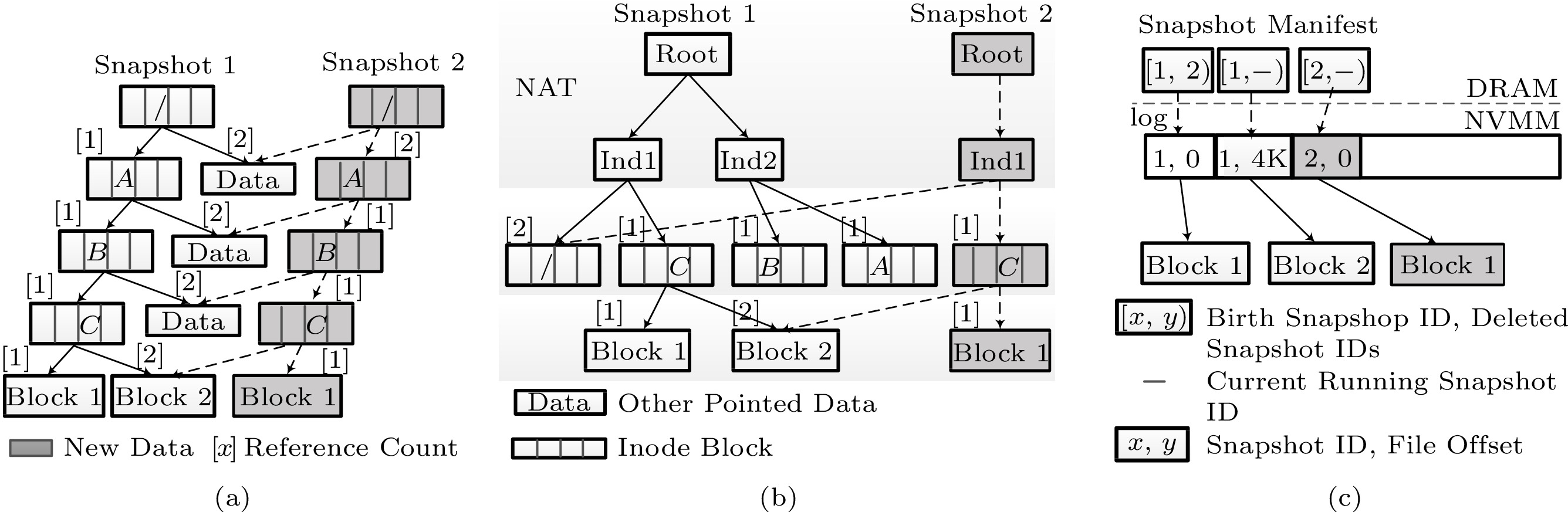
Technologies of snapshots. (a) Snapshots based on COW friendly B-tree. (b) Snapshots of HMVFS. (c) Snapshots of NOVA-Fortis.
Figures of the Article
-
![]() Architecture of several major NVMM file systems. (a) Traditional I/O architecture. (b) NVMM FS architecture. (c) Bypassing VFS architecture. (d) User-level architecture. (e) Using cache architecture.
Architecture of several major NVMM file systems. (a) Traditional I/O architecture. (b) NVMM FS architecture. (c) Bypassing VFS architecture. (d) User-level architecture. (e) Using cache architecture.
-
![]() File data block index structure of (a) ext3, (b) SCMFS, and (c) SIMFS.
File data block index structure of (a) ext3, (b) SCMFS, and (c) SIMFS.
-
![]() File system bandwidth when preforming random (a) read and (b) write operations.
File system bandwidth when preforming random (a) read and (b) write operations.
-
![]() Latency of metadata operations. stat, create, rename and delete use system calls and perform reading, creating, renaming and deleting a file respectively. (a) Cold cache. (b) Warm cache.
Latency of metadata operations. stat, create, rename and delete use system calls and perform reading, creating, renaming and deleting a file respectively. (a) Cold cache. (b) Warm cache.
-
![]() NUMA architecture with two NUMA nodes. APP represents application.
NUMA architecture with two NUMA nodes. APP represents application.
-
![]() Metadata scalability on ext4-dax. ops/s means the number of operations per second.
Metadata scalability on ext4-dax. ops/s means the number of operations per second.
-
![]() Metadata scalability of creating file.
Metadata scalability of creating file.
-
![]() Impact of consistency scalability. N and D represent running on NVMM and DRAM respectively.
Impact of consistency scalability. N and D represent running on NVMM and DRAM respectively.
-
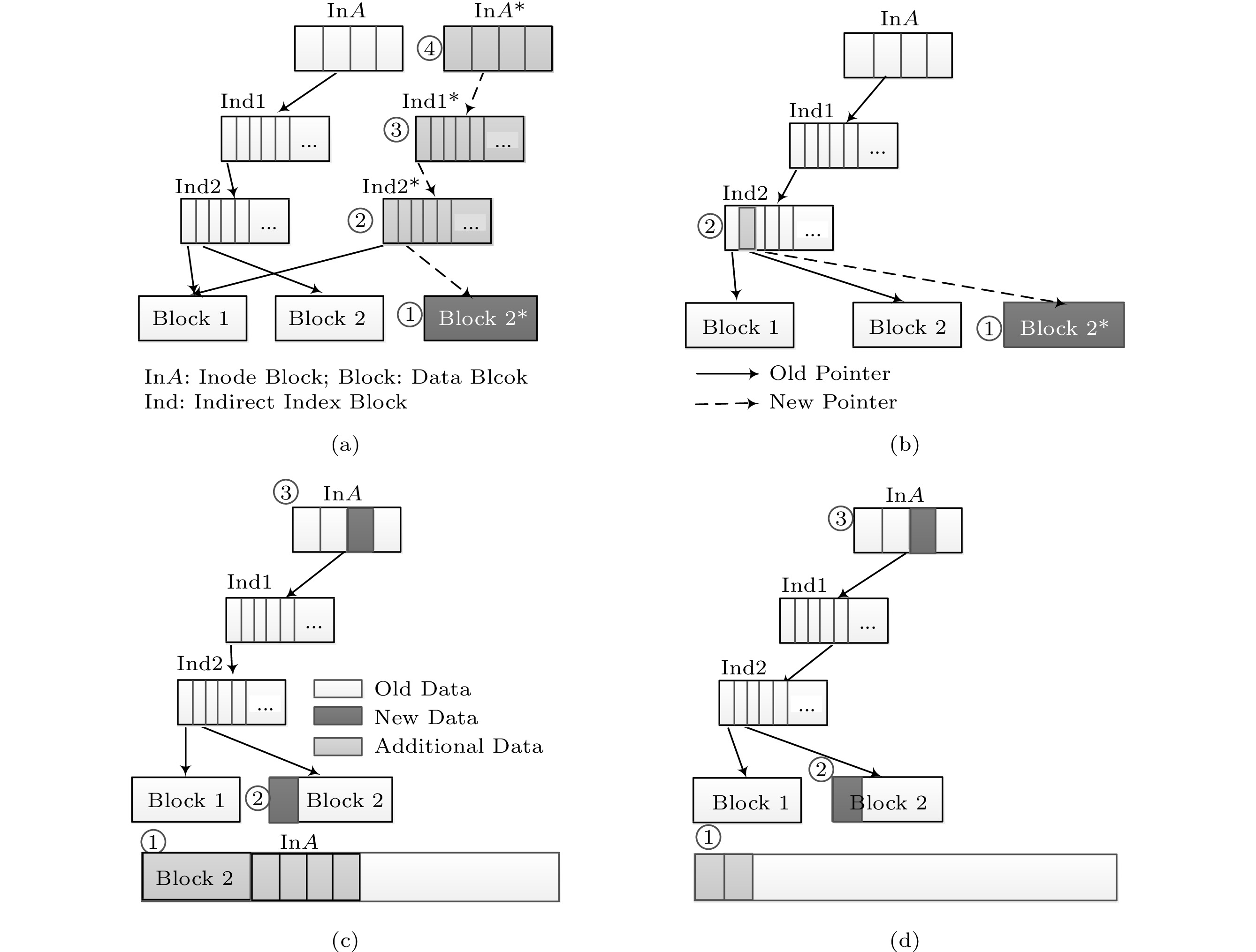
![]() Consistency technology of COW and journaling. Inode block (InA) stores file inodes; indirect index block (Ind) stores directory index; block stores file data; new data: new written data in file system; additional data: extra data caused by writing new data. (a) Traditional COW technique. (b) NVMM COW technique. (c) Traditional journaling technique. (d) NVMM journaling technique.
Consistency technology of COW and journaling. Inode block (InA) stores file inodes; indirect index block (Ind) stores directory index; block stores file data; new data: new written data in file system; additional data: extra data caused by writing new data. (a) Traditional COW technique. (b) NVMM COW technique. (c) Traditional journaling technique. (d) NVMM journaling technique.
-
![]() Consistency technique of log-structuring.
Consistency technique of log-structuring.
-
![]() Technology of soft updates. (a) Traditional soft updates. (b) Soft updates of SoupFS.
Technology of soft updates. (a) Traditional soft updates. (b) Soft updates of SoupFS.
-
![]() Technologies of snapshots. (a) Snapshots based on COW friendly B-tree. (b) Snapshots of HMVFS. (c) Snapshots of NOVA-Fortis.
Technologies of snapshots. (a) Snapshots based on COW friendly B-tree. (b) Snapshots of HMVFS. (c) Snapshots of NOVA-Fortis.
-
![]() Ratio of random read/write latency to sequential read/write latency respectively.
Ratio of random read/write latency to sequential read/write latency respectively.
-
![]() Normalized latency of Optane PMM and Optane SSD against DRAM. 256 B and 16 KB represent the access block size. A and S represent Optane PMM and SSD respectively. (a) Read latency. (b) Write latency.
Normalized latency of Optane PMM and Optane SSD against DRAM. 256 B and 16 KB represent the access block size. A and S represent Optane PMM and SSD respectively. (a) Read latency. (b) Write latency.
Others
-
Chinese PDF
2023-2-10-1054-Chinese Information 27KB -
English PDF
2023-2-10-1054-Highlights 146KB -
Read Online
https://rdcu.be/dhR6a
Related articles
-
2021, 36(4): 806-821. DOI: 10.1007/s11390-021-1344-6
-
2016, 31(3): 561-576. DOI: 10.1007/s11390-016-1647-1
-
2009, 24(6): 1010-1017.
-
2007, 22(5): 641-652.
-
2000, 15(2): 196-201.
-
1999, 14(6): 599-605.
-
1996, 11(4): 405-415.
-
1995, 10(1): 35-41.
-
1994, 9(3): 229-244.
-
1991, 6(4): 347-354.



 Download:
Download: