Worst case of the asynchronous working mechanism. (a) T = 0 s. (b) T = 0.5 s. (c) T = 1 s. (d) T = 10 s.
Figures of the Article
-
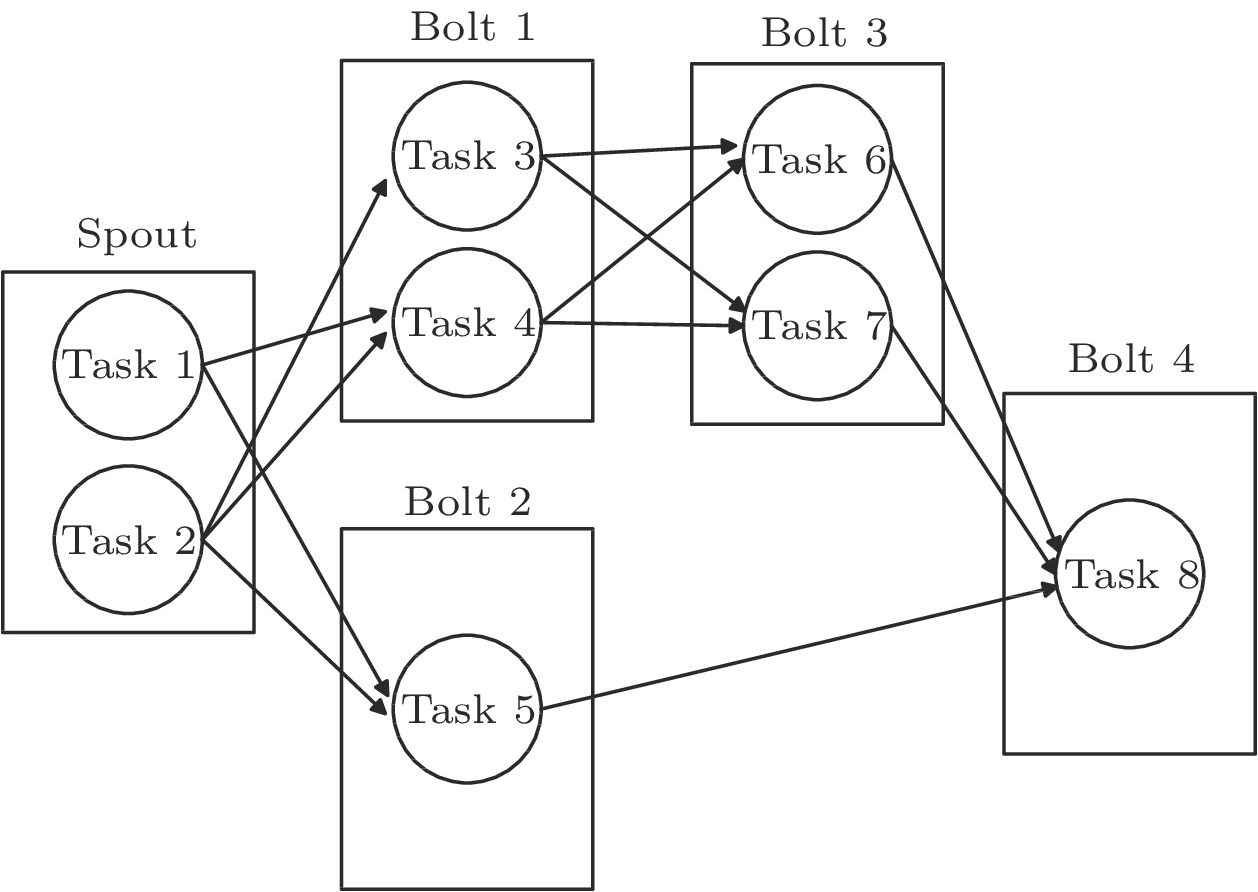
![]() Example of the Storm Topology.
Example of the Storm Topology.
-
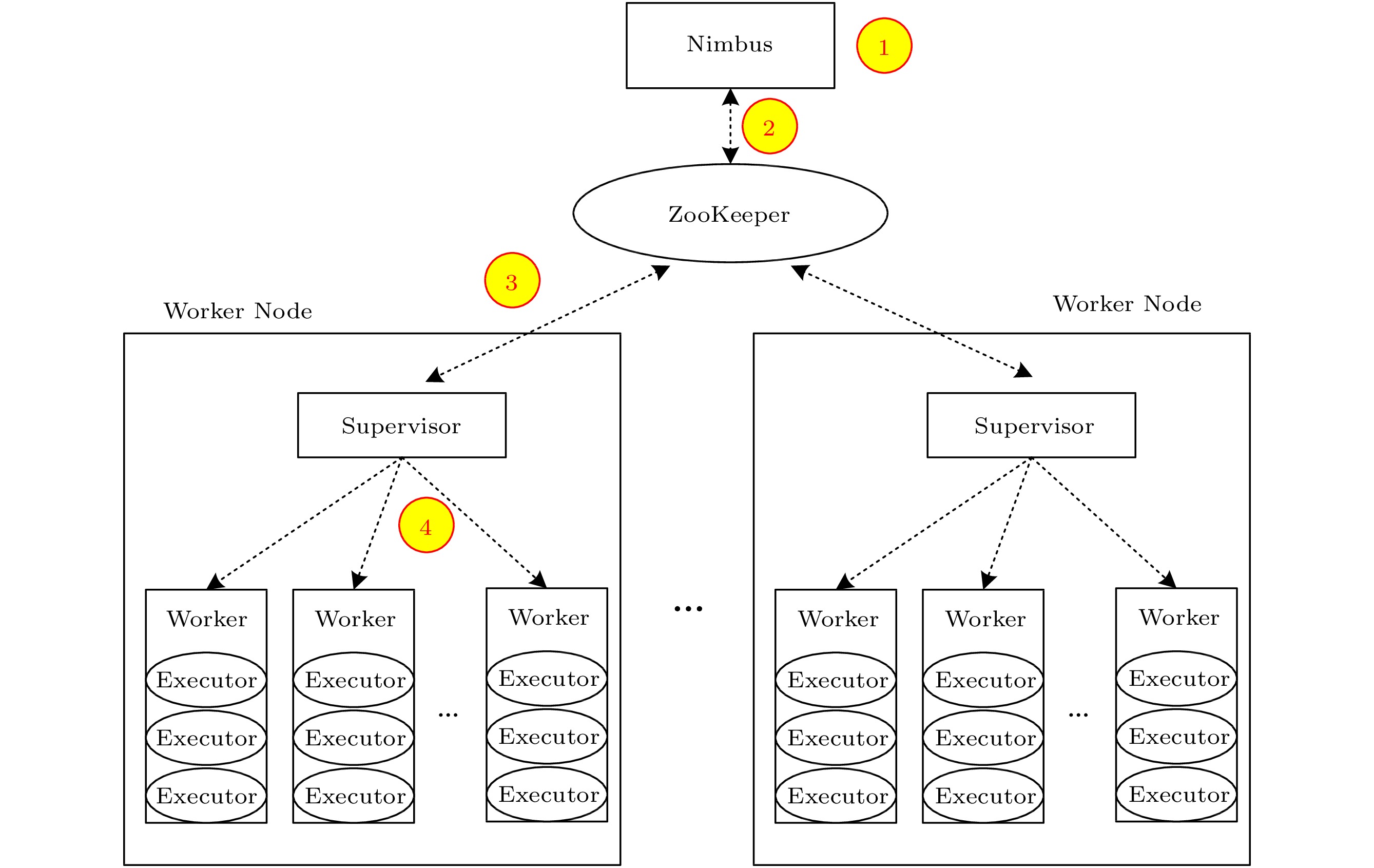
![]() Architecture and task management mechanism of Storm.
Architecture and task management mechanism of Storm.
-
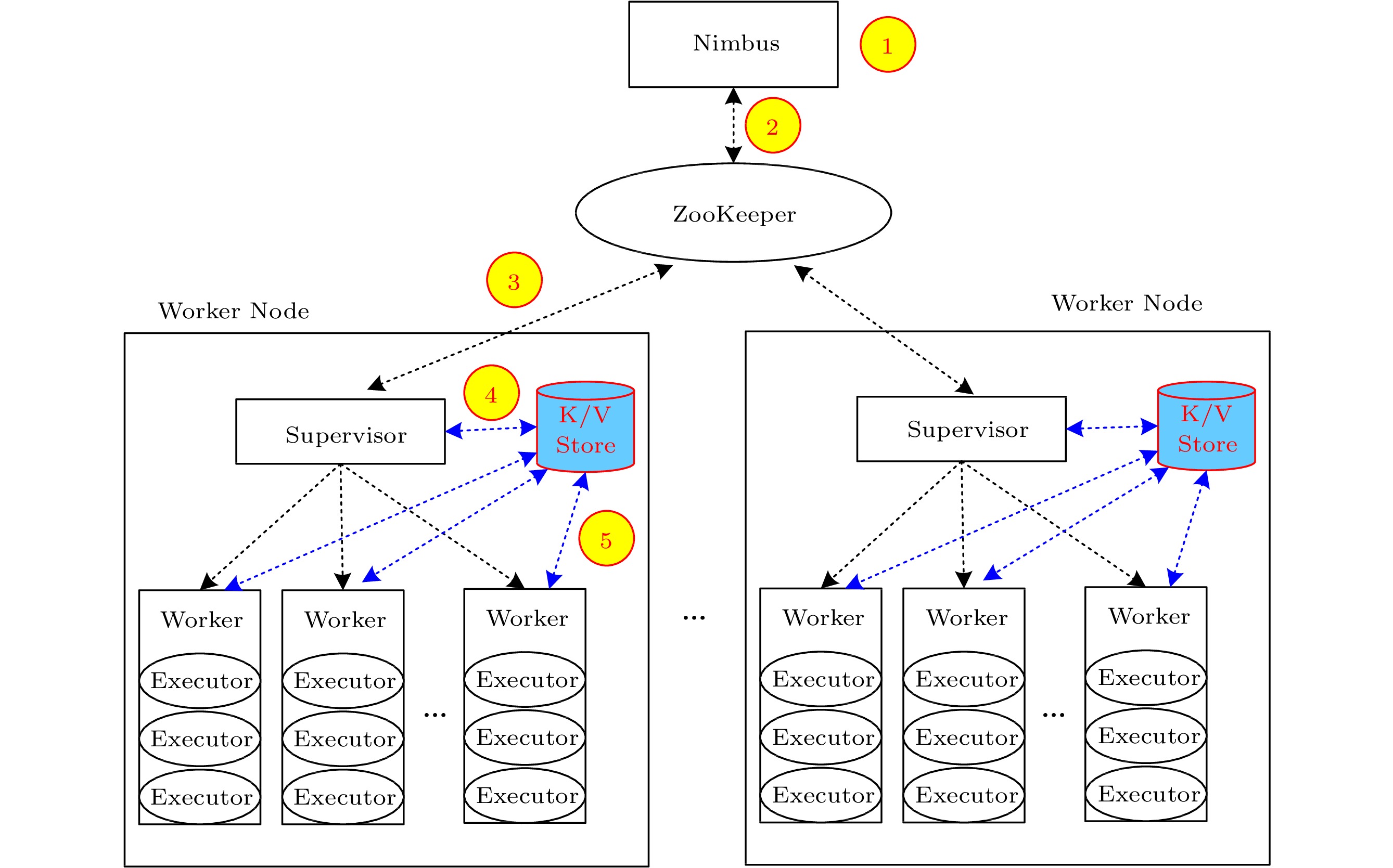
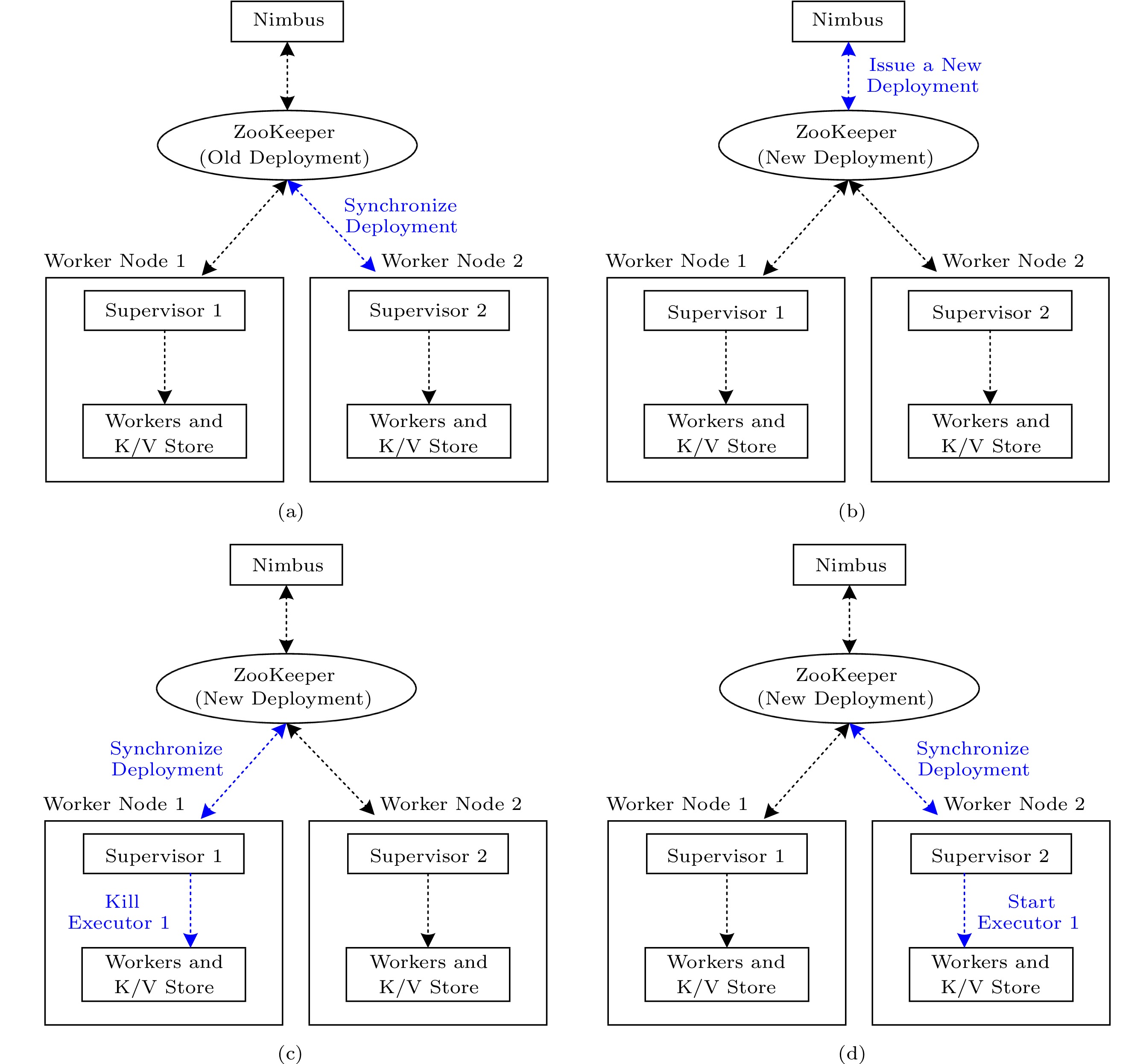
![]() Architecture and task management mechanism of N-Storm. The black dotted arrow is the original control flow of Apache Storm, and the blue dotted arrow is the new control flow of N-Storm.
Architecture and task management mechanism of N-Storm. The black dotted arrow is the original control flow of Apache Storm, and the blue dotted arrow is the new control flow of N-Storm.
-
![]() Worst case of the asynchronous working mechanism. (a) T = 0 s. (b) T = 0.5 s. (c) T = 1 s. (d) T = 10 s.
Worst case of the asynchronous working mechanism. (a) T = 0 s. (b) T = 0.5 s. (c) T = 1 s. (d) T = 10 s.
-
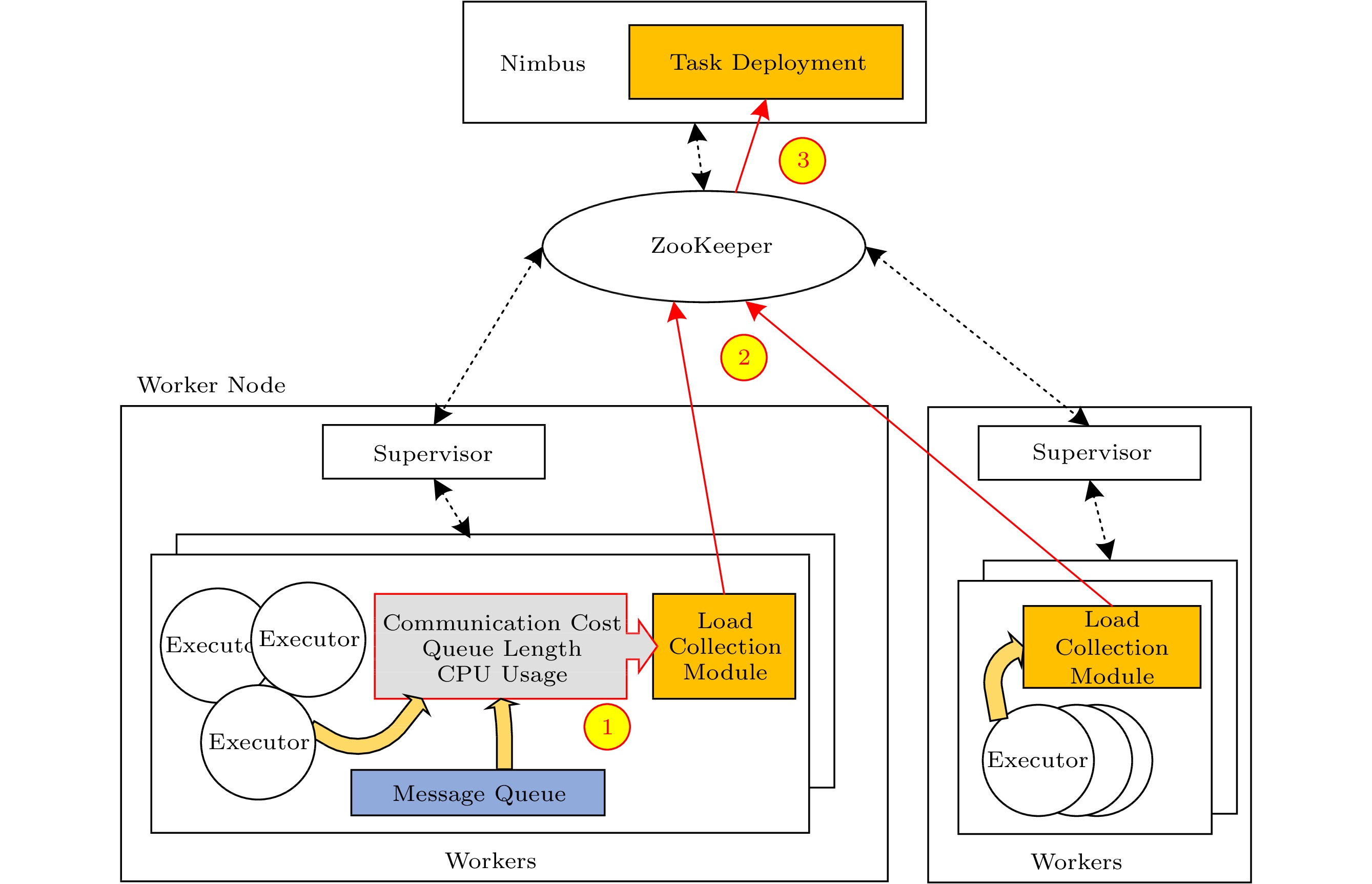
![]() Architecture and load collection flow of OTD. The black dotted arrow is the original control flow of Apache Storm, and the red solid arrow is the new statistical data flow of OTD.
Architecture and load collection flow of OTD. The black dotted arrow is the original control flow of Apache Storm, and the red solid arrow is the new statistical data flow of OTD.
-
![]() Working process of OTD.
Working process of OTD.
-
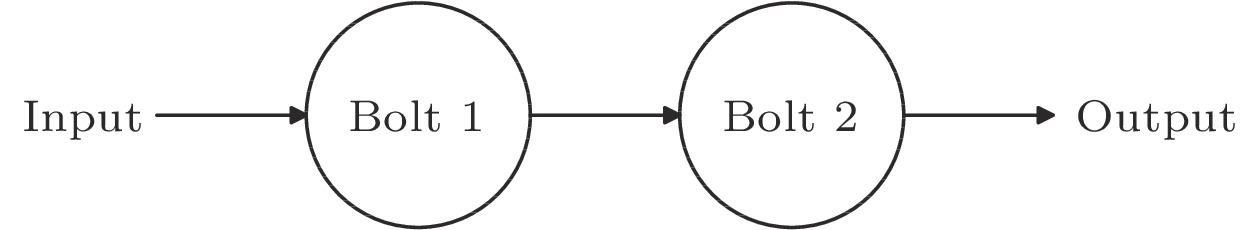
![]() Template of the linear Topology.
Template of the linear Topology.
-
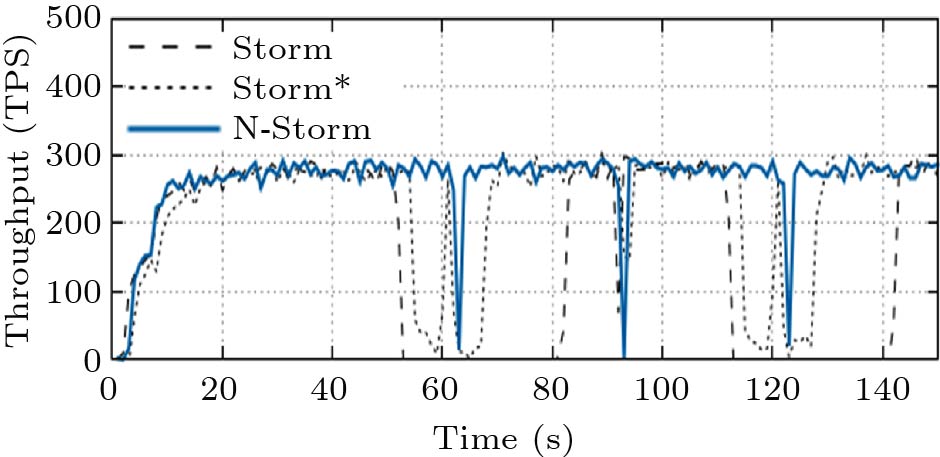
![]() Throughput comparison for the one-task migration.
Throughput comparison for the one-task migration.
-
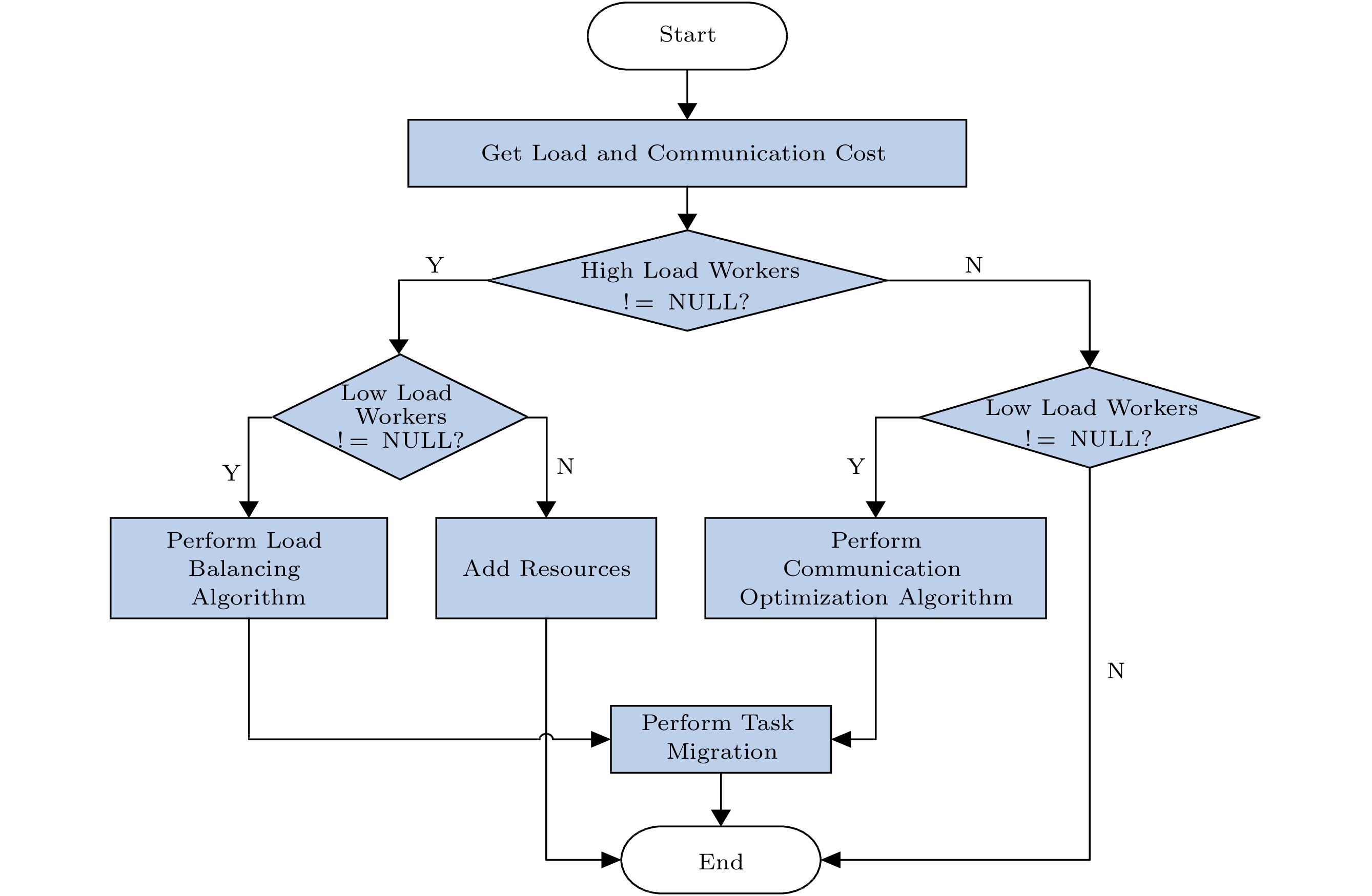
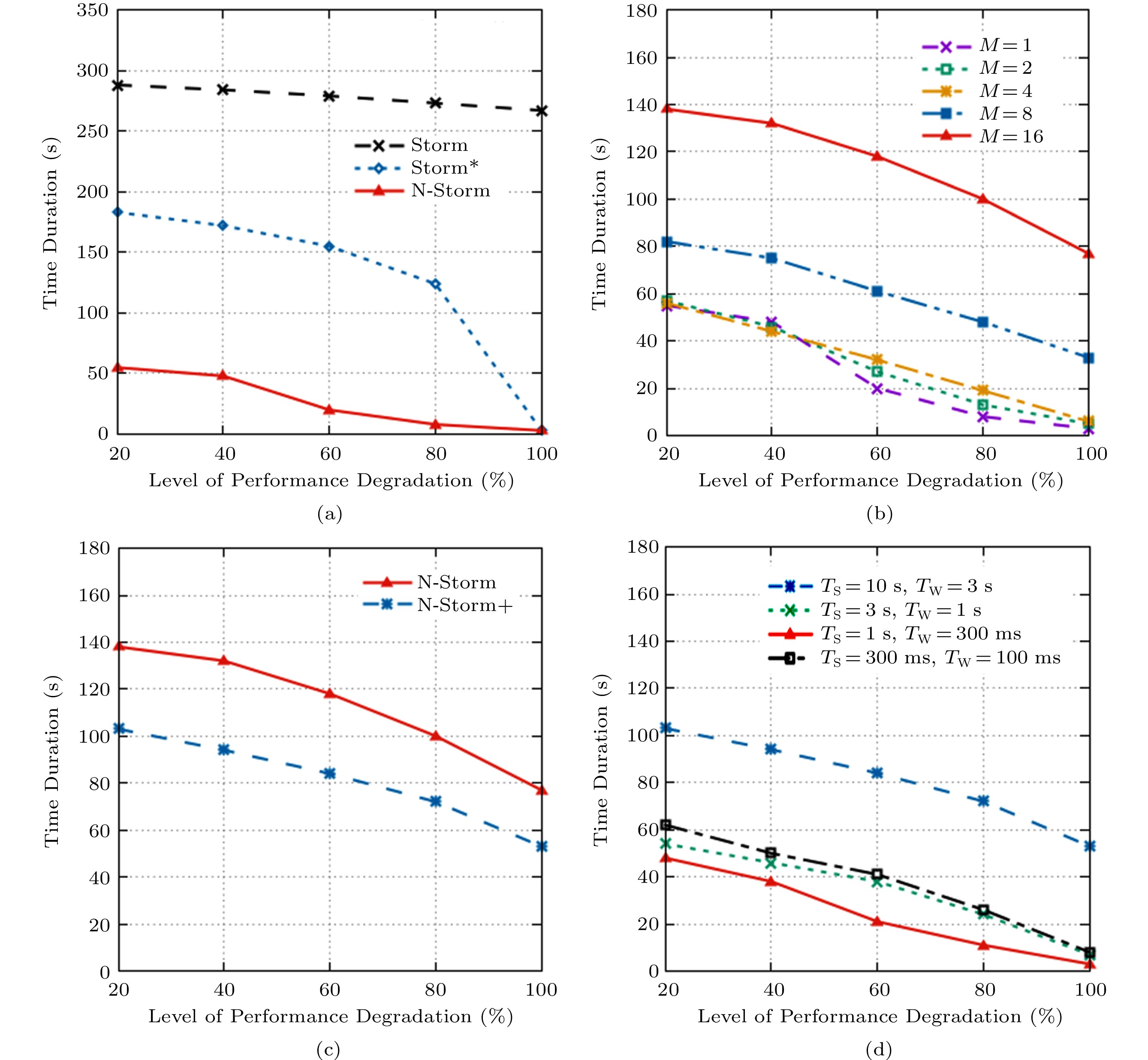
![]() Time duration of performance degradation. (a) One-task migration. (b) Multiple-task migration. (c) Lazy task killing. (d) Impact of TS and TW.
Time duration of performance degradation. (a) One-task migration. (b) Multiple-task migration. (c) Lazy task killing. (d) Impact of TS and TW.
-
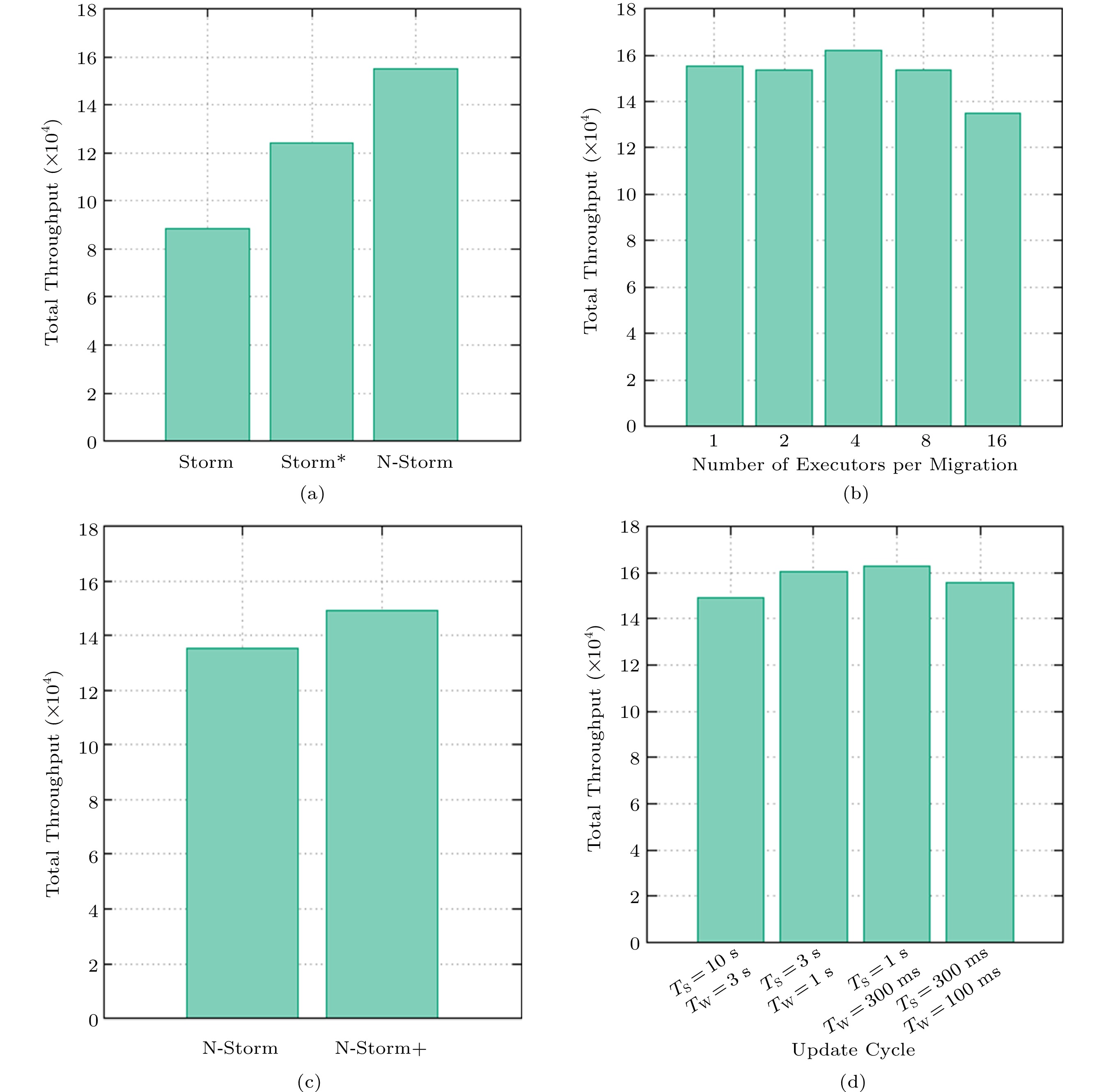
![]() Total throughput during the running of the system. (a) One-task migration. (b) Multiple-task migration. (c) Lazy task killing. (d) Impact of TS and TW.
Total throughput during the running of the system. (a) One-task migration. (b) Multiple-task migration. (c) Lazy task killing. (d) Impact of TS and TW.
-
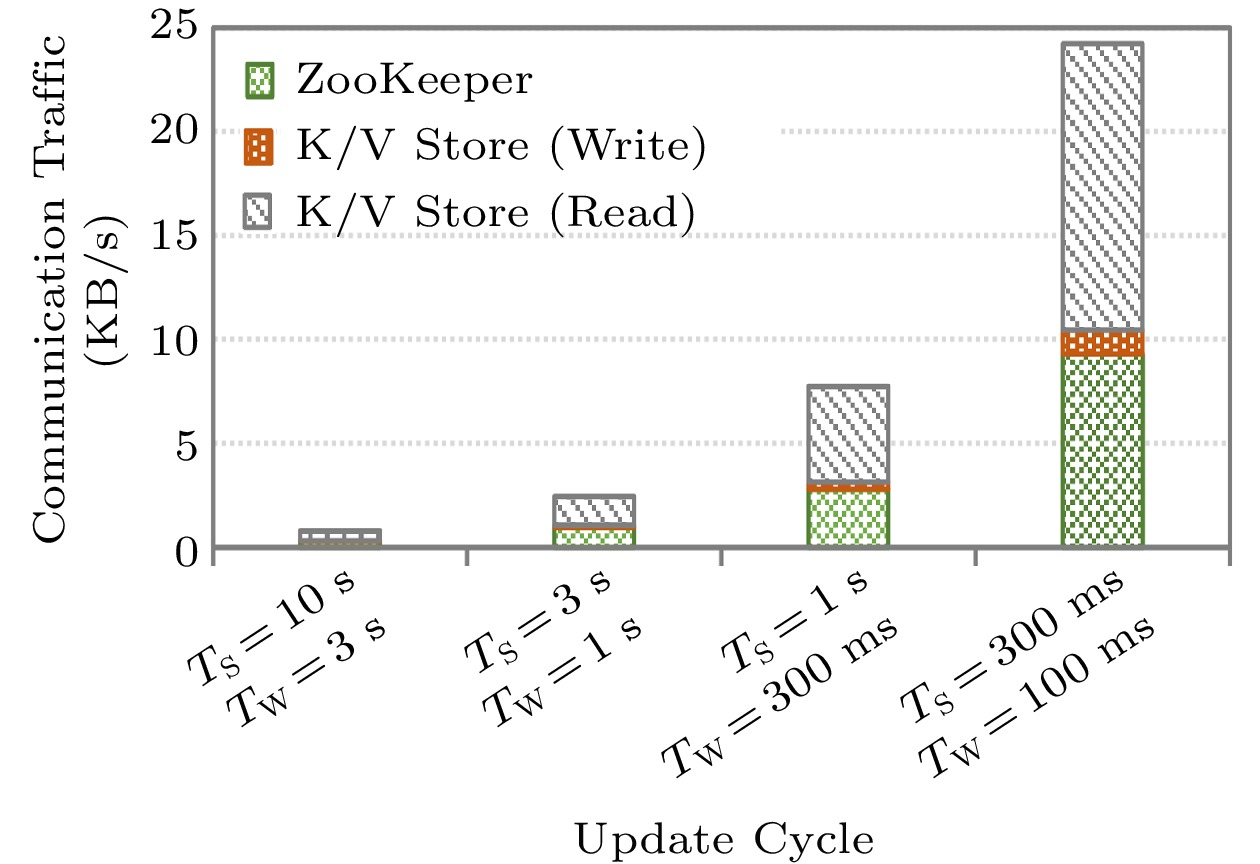
![]() Communication costs of the task management at each Worker node.
Communication costs of the task management at each Worker node.
-
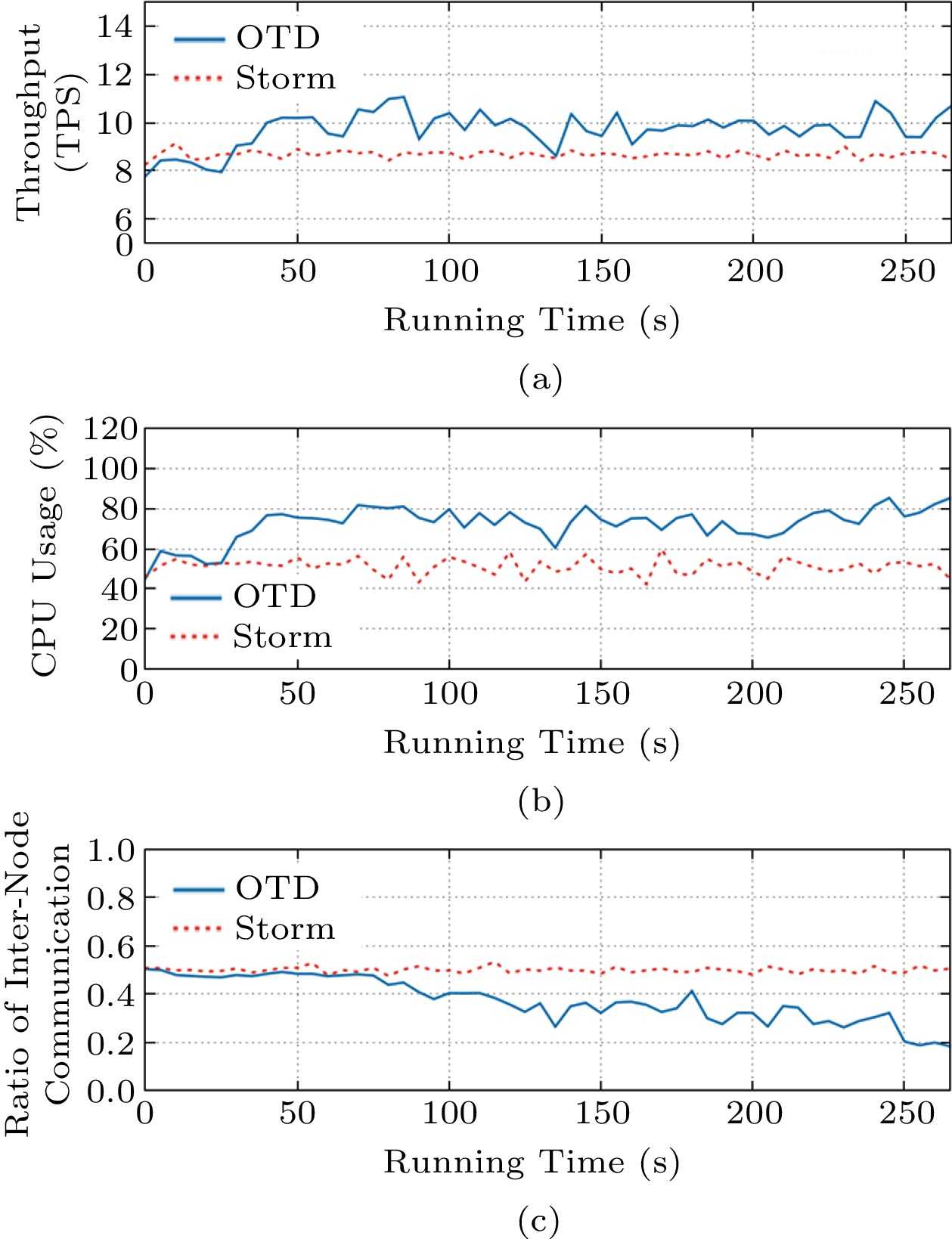
![]() Performance of OTD for computation-intensive applications. (a) Throughput of the system. (b) Average CPU usage of Workers. (c) Ratio of inter-node communication.
Performance of OTD for computation-intensive applications. (a) Throughput of the system. (b) Average CPU usage of Workers. (c) Ratio of inter-node communication.
-
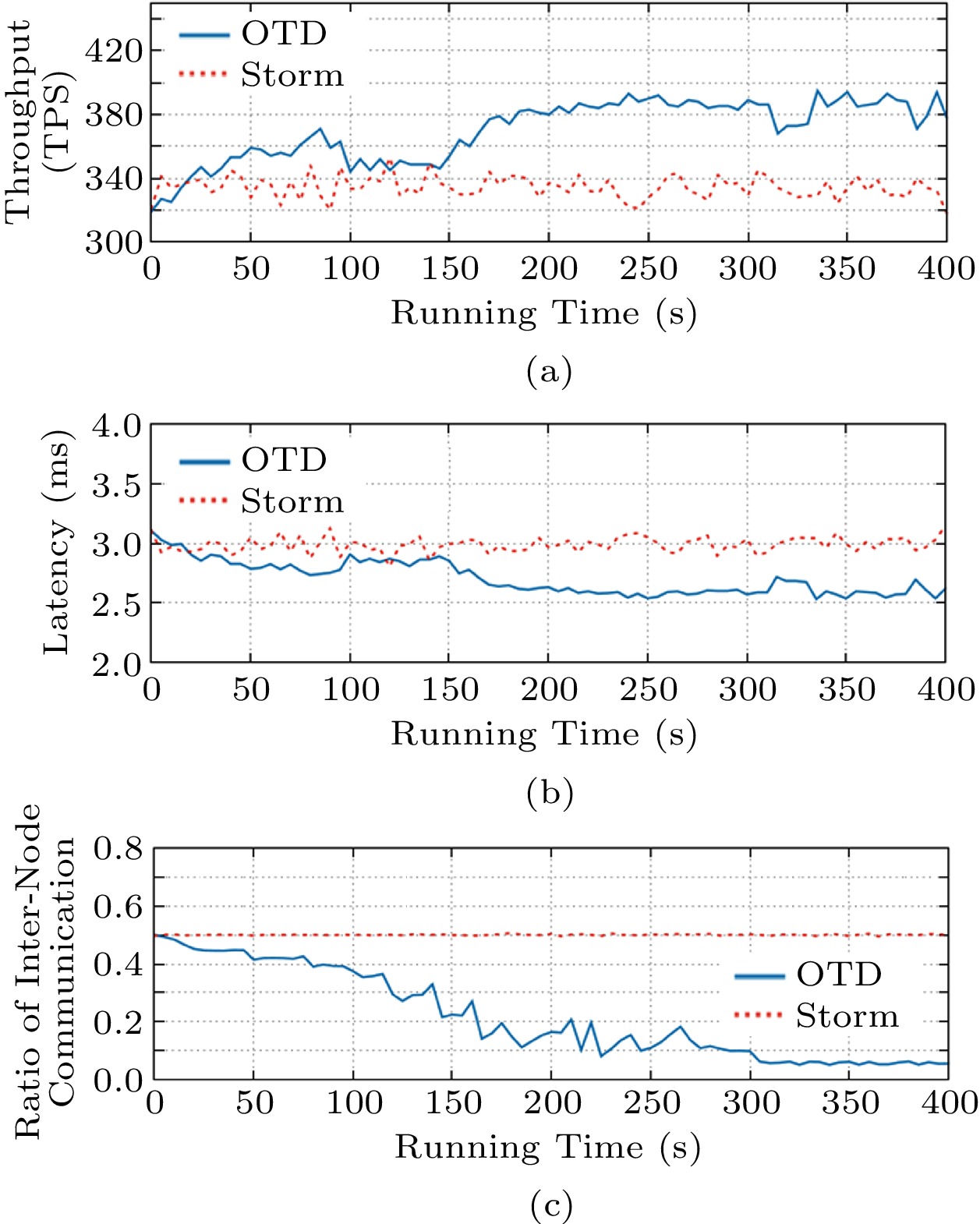
![]() Performance of OTD for communication-intensive applications. (a) Throughput of the system. (b) Average processing delay of tuples. (c) Ratio of inter-node communication.
Performance of OTD for communication-intensive applications. (a) Throughput of the system. (b) Average processing delay of tuples. (c) Ratio of inter-node communication.
-
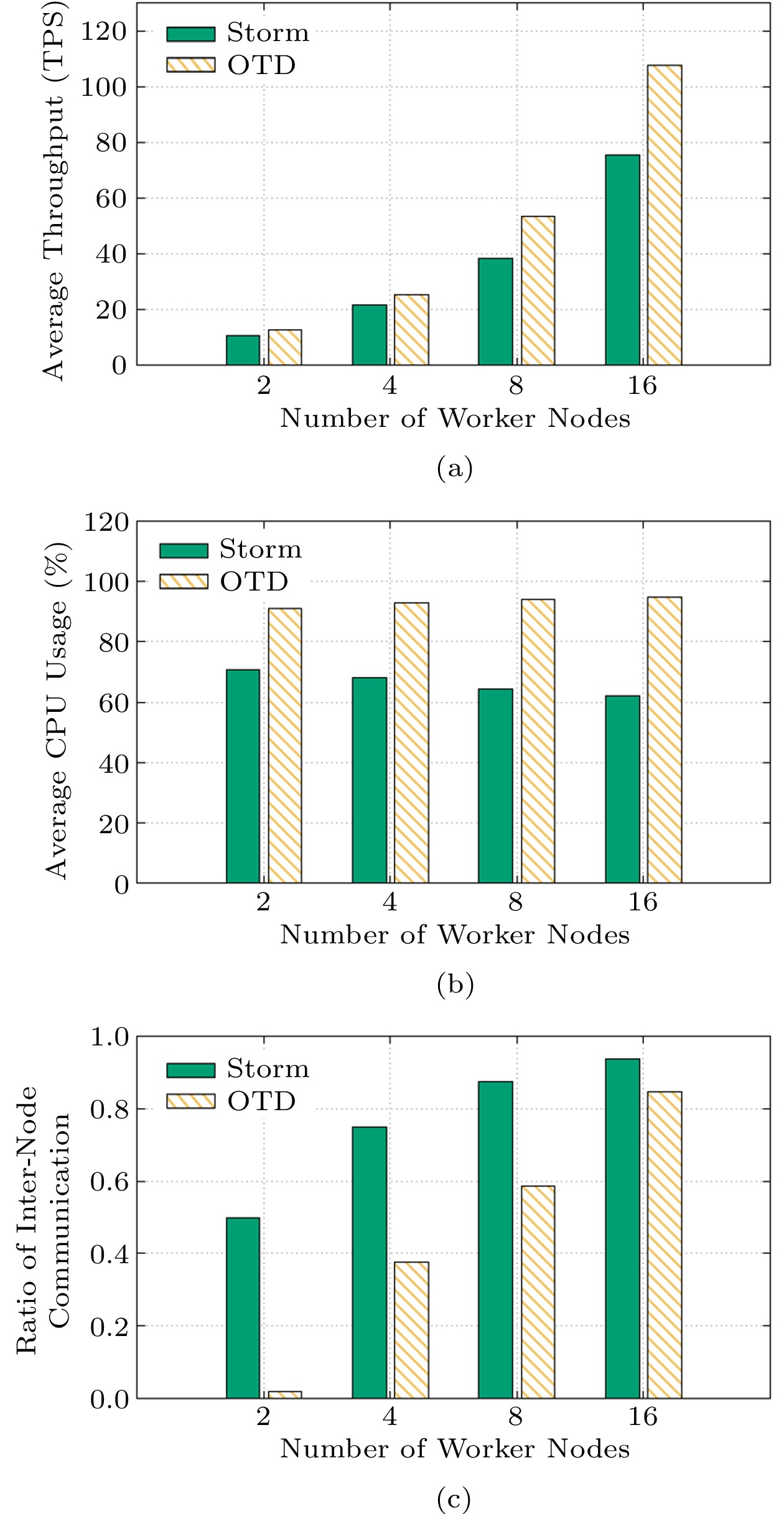
![]() Scalability of OTD for computation-intensive applications. (a) Average throughput of the system. (b) Average CPU usage of Workers. (c) Ratio of inter-node communication.
Scalability of OTD for computation-intensive applications. (a) Average throughput of the system. (b) Average CPU usage of Workers. (c) Ratio of inter-node communication.
-
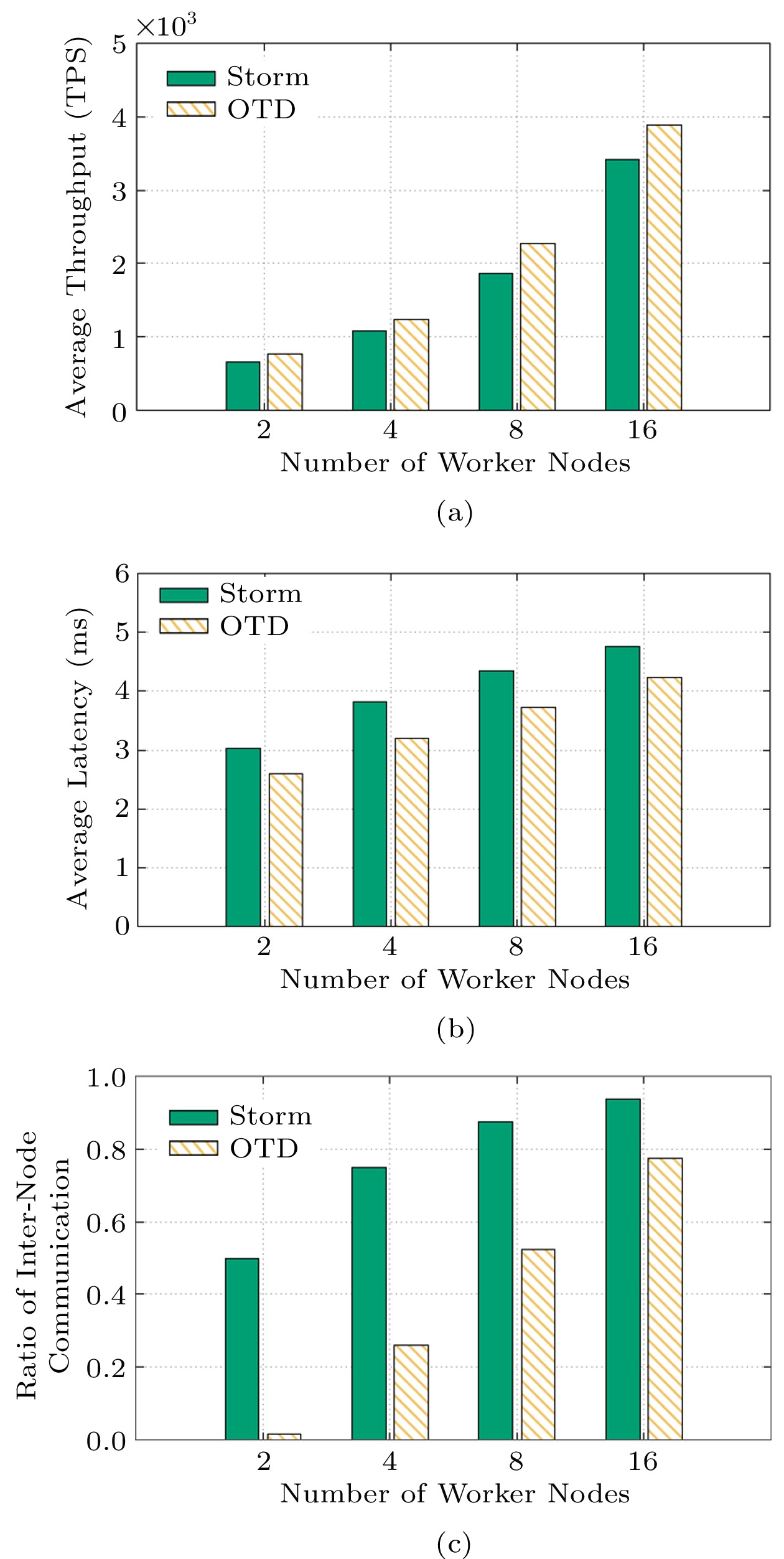
![]() Scalability of OTD for communication-intensive applications. (a) Average throughput of the system. (b) Average processing delay of tuples. (c) Ratio of inter-node communication.
Scalability of OTD for communication-intensive applications. (a) Average throughput of the system. (b) Average processing delay of tuples. (c) Ratio of inter-node communication.
Others
-
External link to attachment
https://rdcu.be/dEw8A -
Compressed file
32KB
Related articles
-
2022, 37(6): 1412-1426. DOI: 10.1007/s11390-021-0730-4
-
2014, 29(3): 519-531. DOI: 10.1007/s11390-014-1446-5
-
2014, 29(3): 345-360. DOI: 10.1007/s11390-014-1436-7
-
2012, 27(3): 492-505. DOI: 10.1007/s11390-012-1238-8
-
2008, 23(2): 203-213.
-
2006, 21(6): 984-988.
-
2000, 15(6): 597-604.
-
2000, 15(3): 295-299.
-
1991, 6(2): 185-194.
-
1987, 2(4): 310-321.



 Download:
Download: