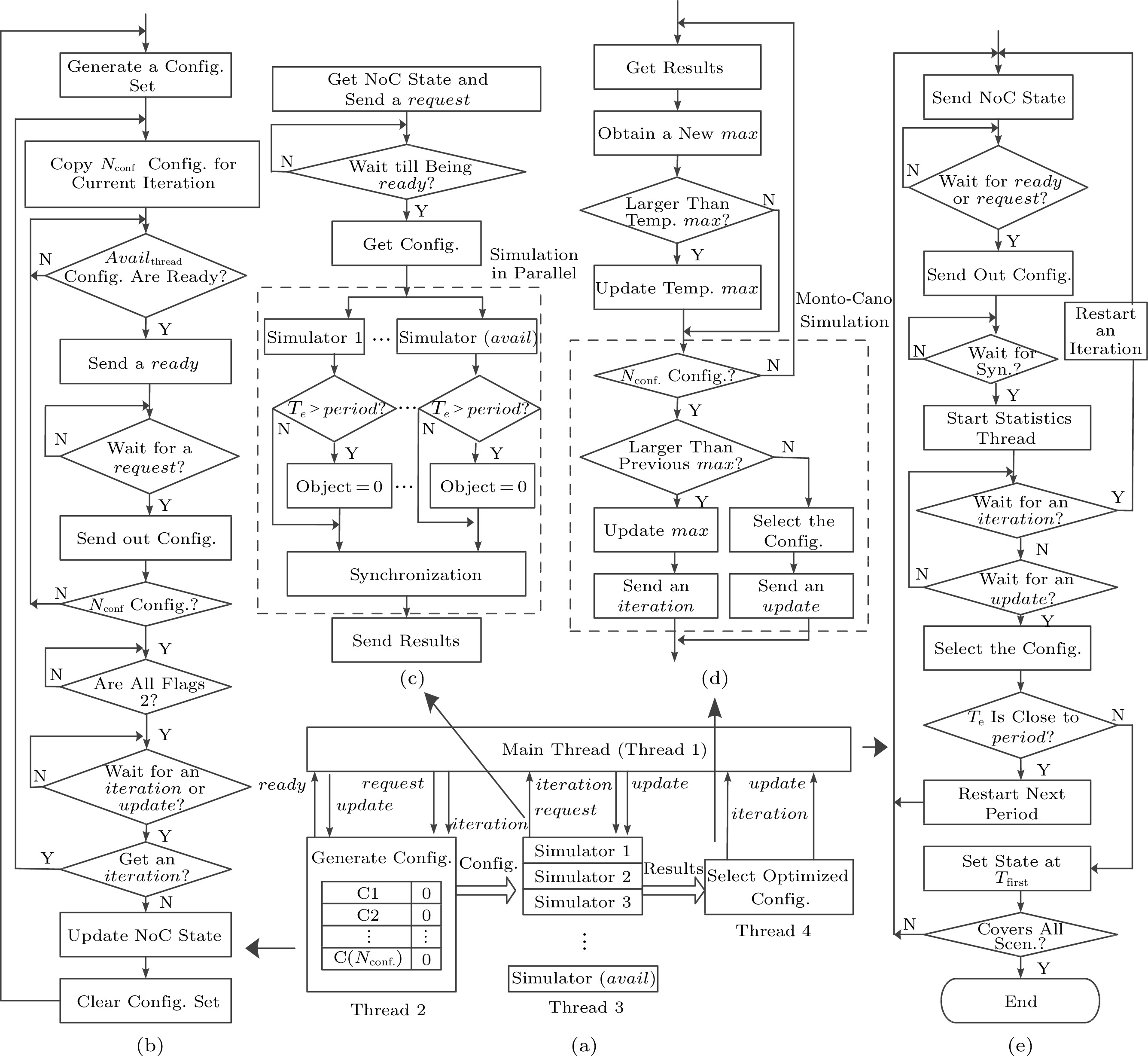
Multi-threading algorithm for generation parallel packets. (a), (b), (c), (d), and (e) are for the algorithm mainframe, configuration thread flowchart (thread 2), simulation thread flowchart (thread 3), statistics thread flowchart (thread 4), and main thread flowchart (thread 1), respectively. Config. means configuration; Temp. means temporary; Scen. means scenarios.
Figures of the Article
-
![]() Flowchart of SBST with BMC[2].
Flowchart of SBST with BMC[2].
-
![]() Constrained ATPG on a sequential circuit.
Constrained ATPG on a sequential circuit.
-
![]() Handshake state machine in a buffer.
Handshake state machine in a buffer.
-
![]() Arbitrating state machine in a switch.
Arbitrating state machine in a switch.
-
![]() Framework of the parallel SBST.
Framework of the parallel SBST.
-
![]() Workflow of the high-level NoC simulator.
Workflow of the high-level NoC simulator.
-
![]() Multi-threading algorithm for generation parallel packets. (a), (b), (c), (d), and (e) are for the algorithm mainframe, configuration thread flowchart (thread 2), simulation thread flowchart (thread 3), statistics thread flowchart (thread 4), and main thread flowchart (thread 1), respectively. Config. means configuration; Temp. means temporary; Scen. means scenarios.
Multi-threading algorithm for generation parallel packets. (a), (b), (c), (d), and (e) are for the algorithm mainframe, configuration thread flowchart (thread 2), simulation thread flowchart (thread 3), statistics thread flowchart (thread 4), and main thread flowchart (thread 1), respectively. Config. means configuration; Temp. means temporary; Scen. means scenarios.
-
![]() Objective values of Monte-Carlo iterations.
Objective values of Monte-Carlo iterations.
-
![]() Iteration number and the sum of cov for the configuration sequence. cov means the coverage rate.
Iteration number and the sum of cov for the configuration sequence. cov means the coverage rate.
-
![]() Fault coverage using different data volumes.
Fault coverage using different data volumes.
-
![]() Heatmaps for fault coverage on different positions using PSBST and the random test. (a)Fault coverage of buffers using PSBST. (b) Fault coverage of buffers using random test. (c) Fault coverage of routers using PSBST. (d) Fault coverage of routers using random test.
Heatmaps for fault coverage on different positions using PSBST and the random test. (a)Fault coverage of buffers using PSBST. (b) Fault coverage of buffers using random test. (c) Fault coverage of routers using PSBST. (d) Fault coverage of routers using random test.
-
![]() Iteration numbers and the sum of cov for the configuration sequence.
Iteration numbers and the sum of cov for the configuration sequence.
Others
-
Chinese PDF
2023-2-13-2553-Chinese Information 30KB -
English PDF
2023-2-13-2553-Highlights 145KB -
External link to attachment
https://rdcu.be/dhR6X
Related articles
-
2014, 29(4): 713-723. DOI: 10.1007/s11390-014-1461-6
-
2013, 28(1): 119-128. DOI: 10.1007/s11390-013-1316-6
-
2007, 22(5): 681-694.
-
2006, 21(6): 907-912.
-
2006, 21(1): 141-146.
-
2000, 15(5): 472-479.
-
2000, 15(1): 84-95.
-
1999, 14(1): 81-87.
-
1998, 13(6): 531-545.
-
1998, 13(1): 79-90.



 Download:
Download:













